磁热疗法是一种快速发展的非侵入性肿瘤治疗手段。National University of Singapore的Jun Ding等人利用热分解法制备了10nm超顺磁性和30nm铁磁性两种Fe3O4纳米颗粒,并利用即表面电荷吸附和酰胺键共价修饰两种方法在Fe3O4 纳米颗粒接入牛血清白蛋白(BSA)分子。初步的溶血和细胞毒性实验表明,表面共轭BSA分子降低了Fe3O4颗粒对红细胞的溶血作用,且对健康的仓鼠肾细胞无细胞毒性。BSA-铁磁性Fe3O4具有高生物相容性:溶血指数<2%,细胞存活率达120%。
这篇综述文章发表于Nano-Micro Letters上2016年第8卷第1期.
全文链接:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40820-015-0065-1
文章引用信息:
Viveka Kalidasan . Xiao Li Liu . Tun Seng Herng . Yong Yang . Jun Ding,Bovine Serum Albumin-Conjugated Ferrimagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles to Enhance the Biocompatibility and Magnetic Hyperthermia Performance,Nano-Micro Lett. Nano-Micro Lett. (2016) 8(1):80–93, http://dx.doi:10.1007/s40820-015-0079-8
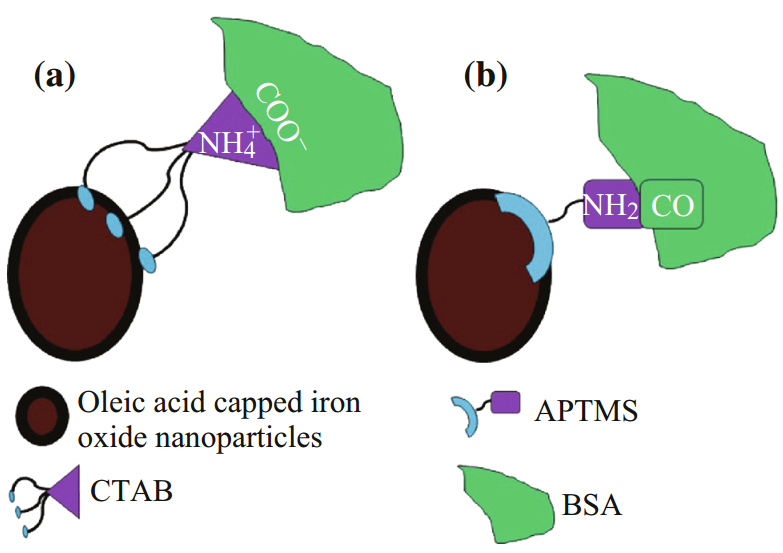
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of (a) physical adsorption of BSA to CTAB; (b) strong covalent amide bond formation between BSA and APTMS
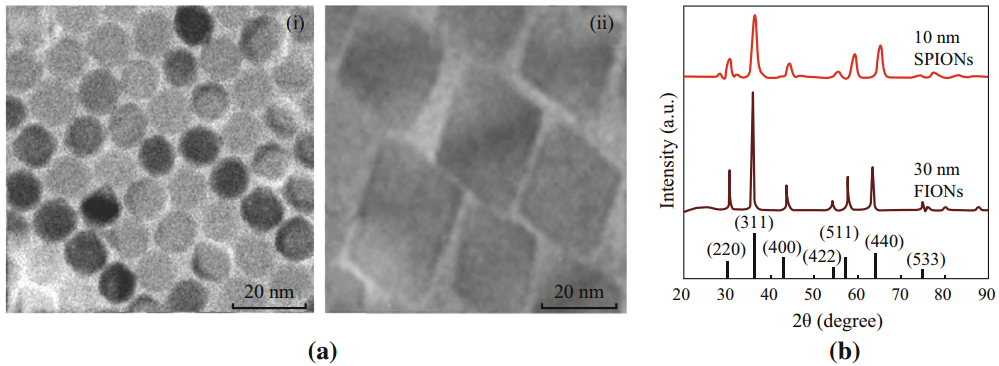
Fig. 2 Characterization of as-synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles( a )TEM images of (i) 10 nm SPIONs and (ii) 30 nm FIONs. (b) XRD plots of SPIONs and FIONs
如果文章对您有帮助,可以与别人分享!:Nano-Micro Letters » 牛血清白蛋白耦联磁性Fe3O4 纳米颗粒提高生物相容性与磁热疗性能
 Nano-Micro Letters
Nano-Micro Letters NML研究文章|癌症标志物检测:基于纳米牛血清白蛋白功能化的石墨烯生物传感器
NML研究文章|癌症标志物检测:基于纳米牛血清白蛋白功能化的石墨烯生物传感器 东南大学滕皋军院士、芮云峰、王乾乾教授等综述:肌肉骨骼系统中的微机器人
东南大学滕皋军院士、芮云峰、王乾乾教授等综述:肌肉骨骼系统中的微机器人 清华大学张萍、卢元等:“光虚拟芯片+人工智能”辅助的冠心病无创诊断
清华大学张萍、卢元等:“光虚拟芯片+人工智能”辅助的冠心病无创诊断